Search
Strengths-based, tiered, accessible, resources and supports (STARS) for Kids for parent, carers and their children.

Access world-leading evidence from Australia’s largest longitudinal birth cohort study, uncovering how early environments influence the development of chronic disease across a generation.
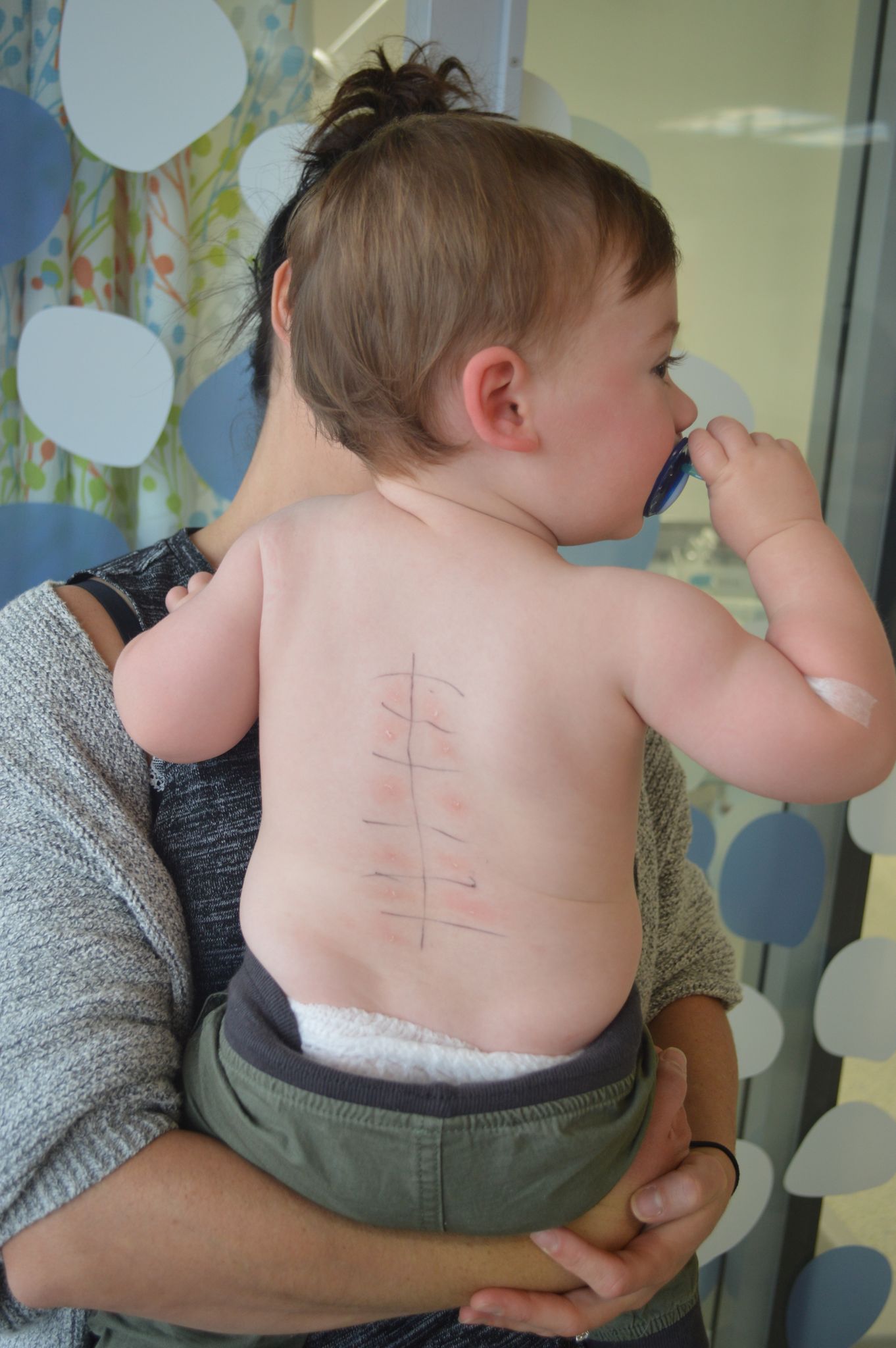
Comparing how mast cells are “programmed” in allergic and non-allergic children at one year of age.

RHINO researchers from The Kids' Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre, will analyse ORIGINS data and turn it into meaningful respiratory and allergy outcome data that can be used by researchers around the world.

The Happy Parenting Program is investigating new ways to provide support to parents with young children from an early age.
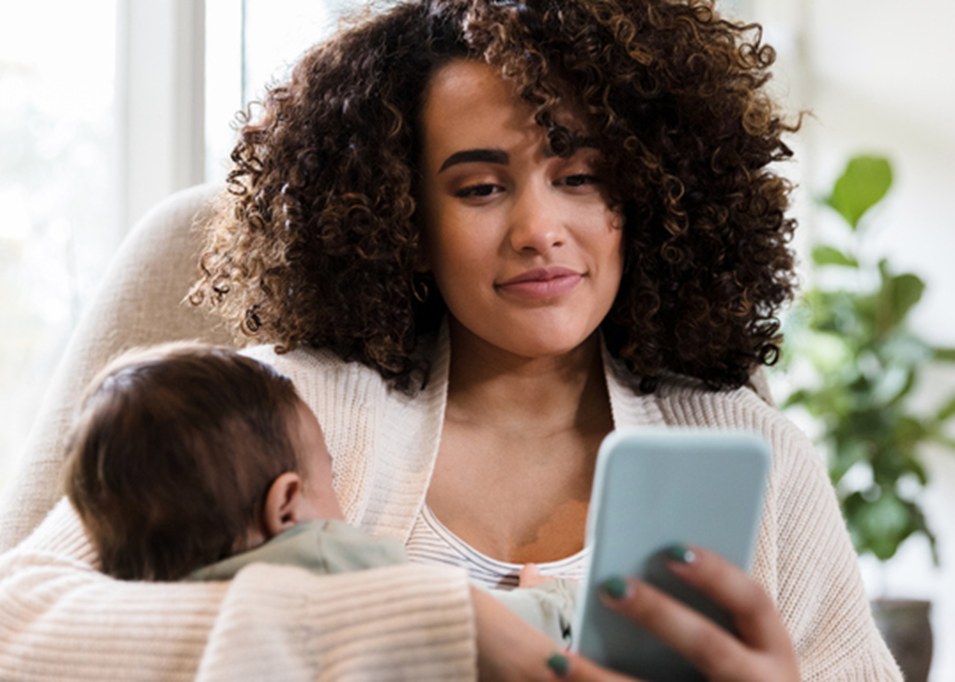

Understanding how families engage with screen technologies and how it may influence child development
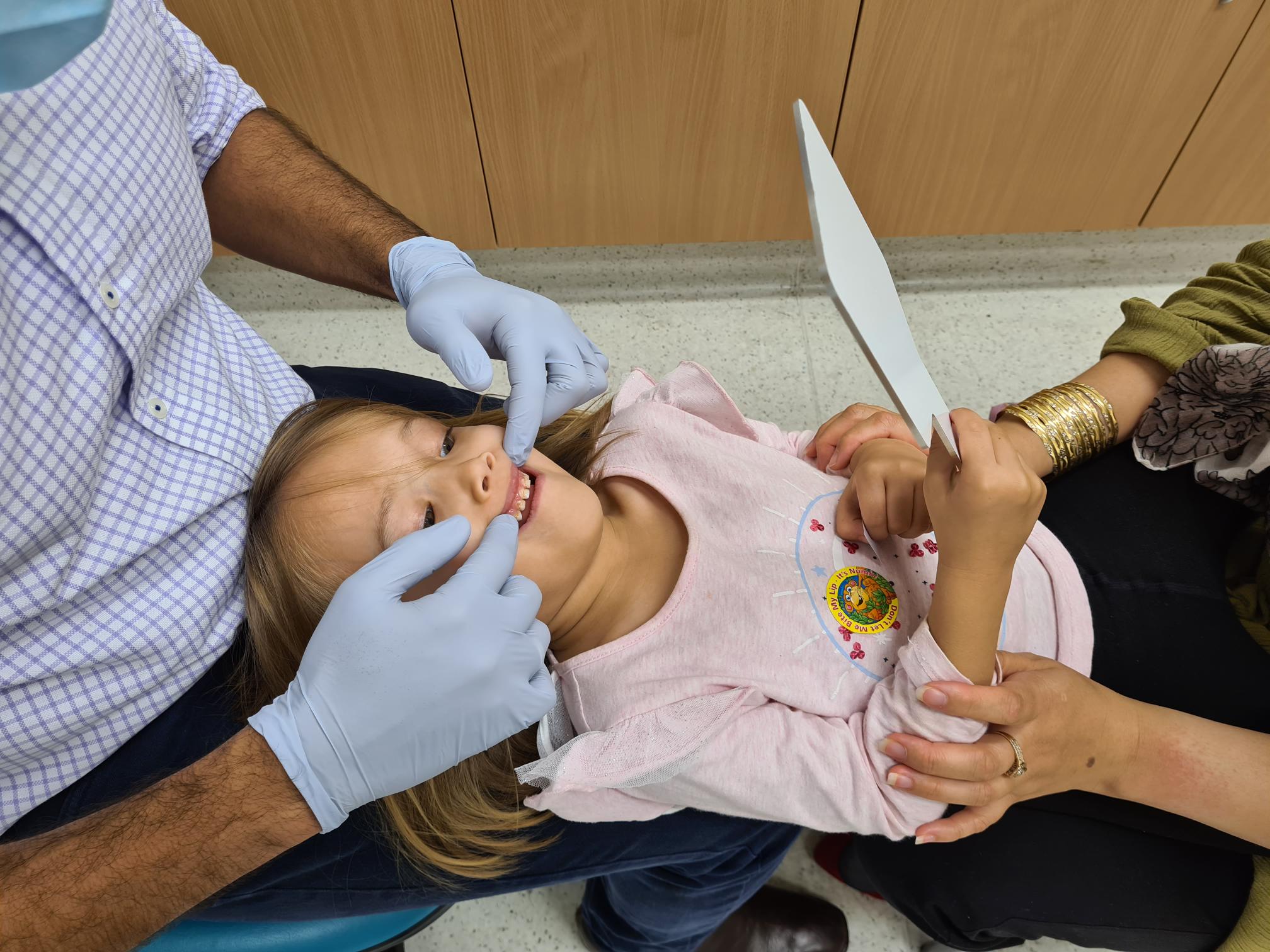
Assessing a dental photographic method as an alternative dental screening method.
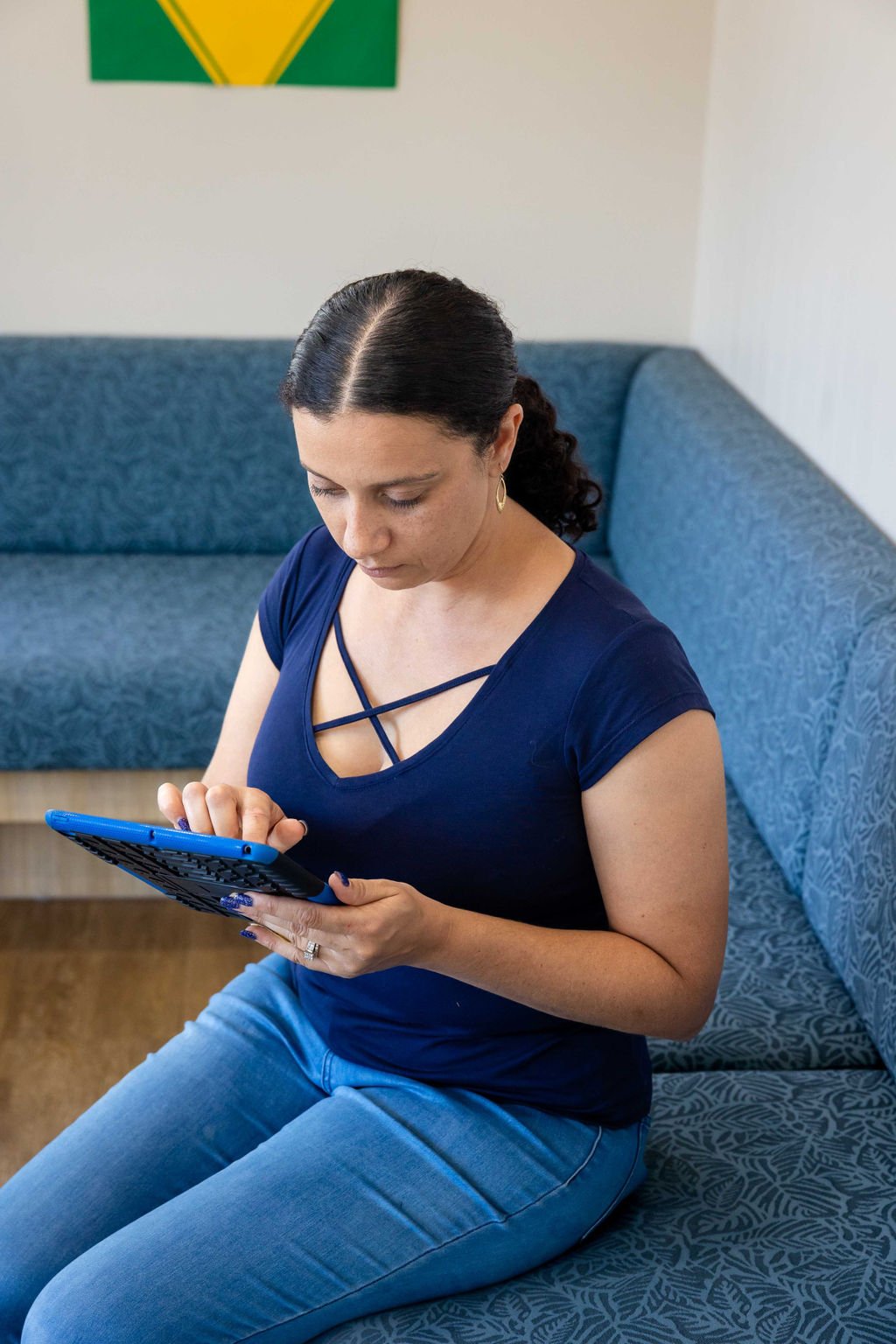

The impact of familial and childhood health conditions on health later in life.
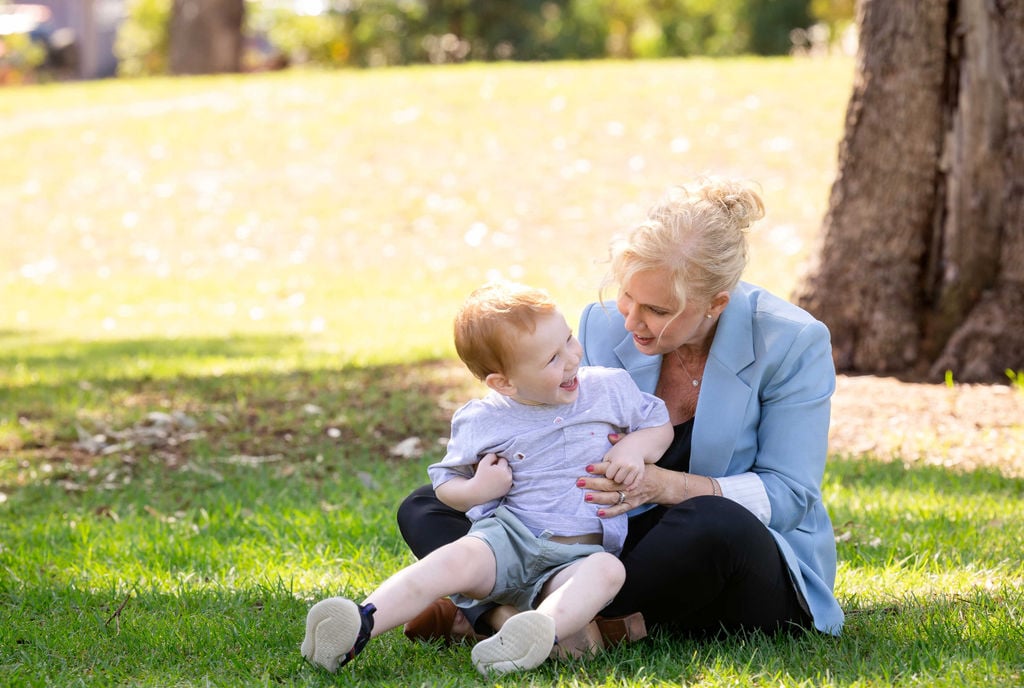

This study is aiming to investigate how sun exposure and time outside impacts the health of your child’s eye and eye growth, over a period of rapid growth in their lives.
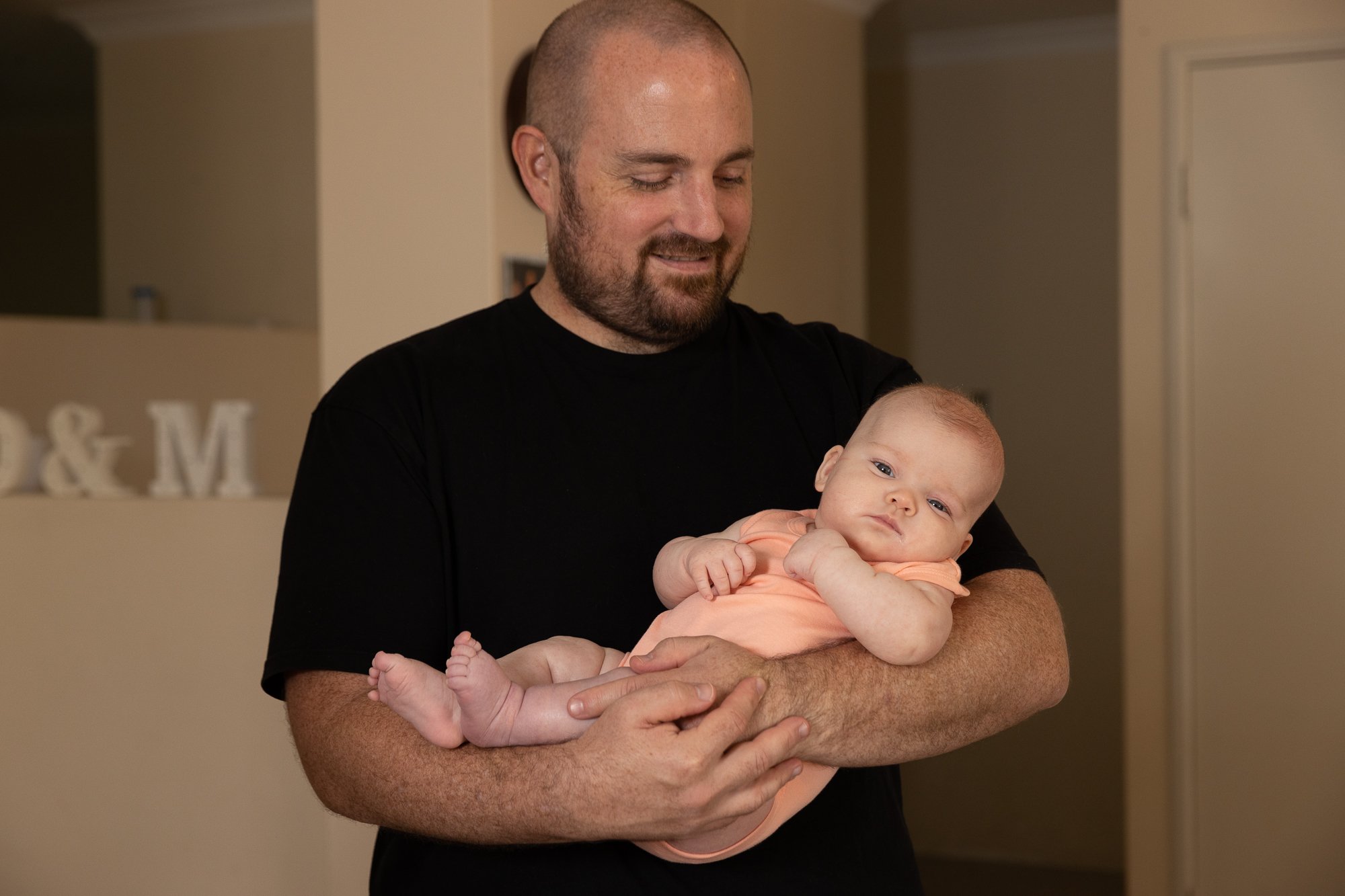

Providing expectant and new Dads with a health check-up
