Search

News & Events
National funding to help foster healthier food environments and fight RHDResearch teams led by The Kids Research Institute Australia have been awarded $3.75 million to support two innovative projects – one focused on pioneering a national ‘Food Atlas’ to map access to healthy and unhealthy food across the country, and the other on developing new ways to prevent Strep throat and rheuma

News & Events
Major grant awarded to tackle antibiotic resistanceVital research aiming to improve the treatment of potentially deadly Group A Streptococcus (Strep A) has been awarded $820,000 in the latest round of National Health and Medicine Research Council’s Ideas Grants.

News & Events
Pneumococcal vaccine sees hospital admissions for deadly pneumonia slashed by halfThousands of children born in Papua New Guinea (PNG) no longer face a future cut short by severe pneumonia, thanks to the introduction of pneumococcal vaccination as part of the country’s National Immunisation Program.
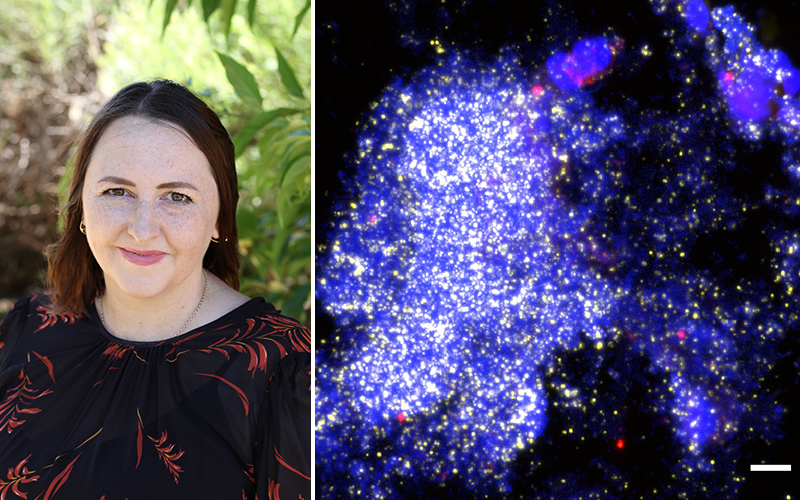
News & Events
Bacterial slime causing persistent wet coughs for childrenResearchers using powerful microscopes have identified bacterial slime in the lungs of some children with persistent wet coughs.

News & Events
Raine Foundation grants to support key child health researchThree outstanding young researchers from The Kids Research Institute Australia have been named Raine Fellows and received valuable Raine Priming Grants to support their child health research.

News & Events
Co-ordinated approach urgently required to slow progression of antibiotic resistanceAboriginal mum and child

News & Events
National guideline to tackle record rates of skin infectionResearchers have developed the first National Healthy Skin Guideline to address record rates of skin infections in Australia’s Indigenous communities.

News & Events
Rheumatic heart disease remains a major killer in Oceania regionA new study shows that people living in the Oceania region, including Australia, have the highest risk in the world of dying from rheumatic heart disease.
News & Events
New recommendations to stop antibiotics soonerThe Kids researchers are amongst a group of experts who have recommended that doctors can stop intravenous antibiotics sooner in children.

News & Events
Gastro gap between Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal children shrinkingThe world's largest study of gastroenteritis trends in children has shown the disparity between Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal health may be improving.
